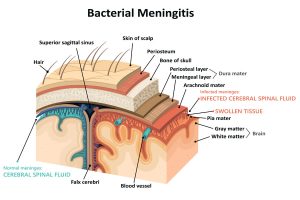
Antibiotic resistance is a significant issue because it can quickly make antibiotic therapy ineffective. Extensively and pan drug-resistant bacteria are extremely hard to eradicate. The therapy requires longer hospital time and incorporation of drug combinations which causes more adverse reactions and puts a burden both on the healthcare system and the individual.
Because of globalization, infections nowadays spread easily around the globe. For example, methicillin-resistant S. aureus, or MRSA, antibiotic resistance has been reported in hospitals around the globe. MRSA infection can spread to the bloodstream, heart, and lungs, causing life-threatening conditions.
Without addressing antibiotic resistance we can potentially see a pandemic of an untreatable disease. Not to mention a dark future when common conditions and minor wounds can lead to death, just like in medieval times.
What is Antibiotic Resistance
Antibiotic resistance, AR for short, is a microorganism’s ability to withstand the effect of an antibiotic. As a result, the bacteria cannot be eradicated with otherwise effective medication. The infection caused by such bacteria becomes persistent and can lead to various complications. According to the CDC, over 2.8 million infections caused by pathogens with antimicrobial resistance occur yearly in the USA.
How antibiotics work
The antimicrobial effect of antibiotics can work in two ways:
- The drug impedes cell growth. It is called bacteriostatic action and is achieved through certain processes in the cell’s metabolism, such as protein synthesis or DNA replication.
- Bactericidal medications, on the other hand, kill the pathogen cells. They target peptidoglycans—molecules in cell walls and disrupt them.
Mechanism of Antibiotic Resistance
There are three main mechanisms of antibiotic resistance.
Mutation
Some strains of bacteria are especially prone to adaptive mutation. The aforementioned Staphylococcus aureus is one of them. The genetics of the bacteria changes providing them more protection from the pharmacological action of the drug.
Natural Selection
The mechanism of natural selection is basically “the fittest lives”. Genes of the pathogens that survived antibiotical treatment get passed to new cells and that can make an antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
The main reason why antibiotic therapy did not achieve full eradication of pathogens, is improper use of antibiotics: wrong administration, dosage, incomplete course, etc.
Horizontal Gene Transfer
A non-resistant bacteria cell can receive genetic information from an AR pathogen. The process of transmission is called horizontal gene transfer. There are several mechanisms of it:
- Transformation—bacteria pulls DNA fragments from the environment. It can be DNA shed by an AR cell.
- Conjugation—the genetic information is transferred from one pathogenic cell to another when they are close enough.
- Transduction antibiotic resistance occurs when the DNA has been accidentally transferred to a bacteria by a bacteriophage virus.
Antibiotic Resistance Causes
As you can see from the mechanisms, AR has natural development. However, misuse of antibiotics drastically increases the speed of the process. Therefore, it is considered the main cause of AR development and, thus, the main threat to the antibiotics’ efficacy.
Additionally, new antibacterial medications to which infections are not yet resistant, are developed very slowly. The process of medication creation takes up years for the drug to be safe and effective—while a single incomplete course can create a resistant infection.
Addressing Antibiotic Resistance
In order to avoid and reduce AR, governments and global organizations develop policies, create initiatives, and promote awareness about the issue. There are worldwide and national action plans in force that pursue two main goals.
Prudent use of antibiotics
Antibiotic stewardship is a set of measures aimed to improve how antibiotics are prescripted by doctors and used by patients. It can be implemented through federal and national regulations and educational activities that spread valuable information on the matter. Proper use of antibiotics includes:
- No administration to plants or animals to promote growth and prevent diseases. Veterinarians only prescribe antibiotics in the event of an infection.
- Doctors prescribe medication following strict protocols and only if the need is present; antibiotics cannot be legally obtained without a prescription;
- Patients should use antibiotics responsibly: only if prescribed by a doctor; carefully following instructions; never sharing or saving antibiotics; undergoing a full treatment cycle.
Infection prevention and control
Preventative care plays a significant role in combat against AR. Prophylactic measures reduce the necessity to use antibiotics and, thus, the risk of pathogens becoming resistant to them. Such measures include:
- Vaccinations;
- Proper hygiene (such as washing your hands, using sanitizers, not sharing personal items, etc.);
- Social measures (wearing a mask if sick, covering your mouth with an elbow when sneezing or coughing, social distancing, etc.).
Summary
Antibiotic resistance is an occurrence when the pathogen does not respond to treatment properly. It requires longer and stronger treatment and increases the possibility that the disease will become untreatable. AR compromises the efficacy of therapy and poses a threat of new global pandemics. Proper use of antibiotics and preventative measures against infections are key factors in reducing AR.
FAQ
How is antibiotic resistance treated?
Diseases caused by AR pathogens are managed through intensive treatment that combines several most modern medications.
How do you reverse antibiotic resistance?
While AR likely cannot be fully reversed, we can slow the process down.
What is the most promising approach for managing antibiotic resistance?
Control and prophylactic of infectious diseases and responsible use of antibiotics are the most perspective methods to inhibit Ar development.
What are 2 strategies the US is using to combat antibiotic resistance?
CDC calls for aggressive preventative measures and heavily controlled use of antibiotics.