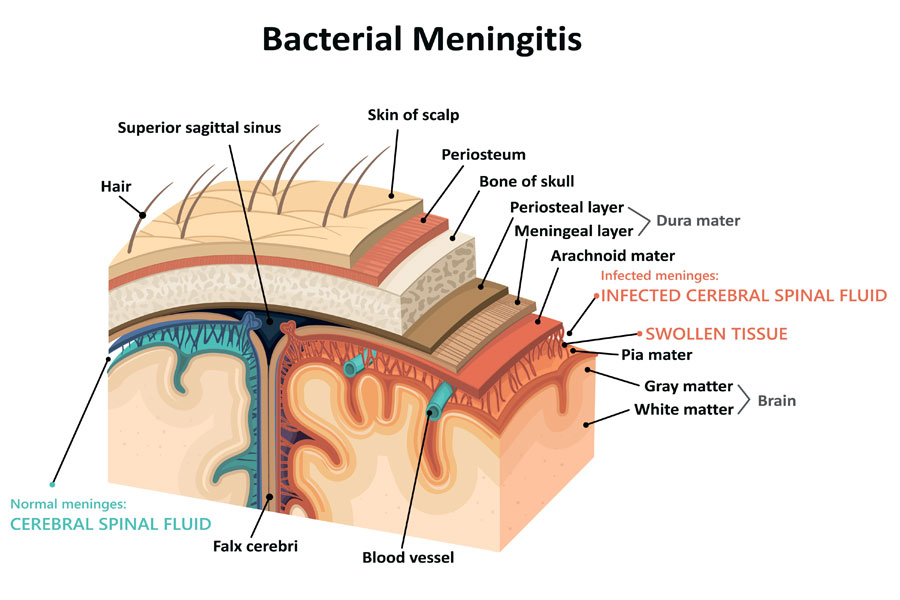
Bacterial meningitis is a very serious health issue caused by a variety of bacteria. It is a form of inflammation in the spinal cord that affects the brain. The disease affects the surrounding cerebrospinal fluid and meninges (membranes). Bacterial meningitis can lead to drastic health consequences and, on some occasions, death.
The disease progresses fast and can result in lethal cases within several hours of the first symptoms. In other cases, the disease can have permanent or long-lasting physical effects, including hearing loss or brain damage. It can be spread among adults and children, leaving the latter the most at-risk group.
Types of Bacterial Meningitis
Depending on the bacteria that lies in the root of the disease, bacterial meningitis can be divided into four main types. These are:
- Listeria monocytogenes – food bacteria;
- Streptococcus pneumoniae – bacteria that affects the respiratory tract the most;
- Meningococcal meningitis – easily-spreadable bacteria that is found in respiratory fluids;
The difference in these types helps identify the correct treatment and possible ways of getting infected. However, there are more known types of bacteria that trigger the disease, including Neisseria meningitidis or Escherichia coli (often found among newborns).
Symptoms
First, there is a difference between viral and bacterial meningitis. The latter is usually more severe and begins more suddenly and rapidly than the former. Hence, it is also considered to be more dangerous. Both types may start similarly. Yet, bacterial meningitis progresses much faster. In addition, the symptoms will be somewhat similar among children and adults, unlike with viral meningitis.
Here is the list of symptoms you should be aware of:
- Nausea and vomiting;
- fever;
- headache;
- stiff neck;
- irritability;
- chills;
- lethargy;
- sensitivity to light;
- sense of confusion and disorientation;
- ‘bruising’ in random areas.
Overall, patients have no way of knowing which type of meningitis they have based on the group of symptoms. Only doctors can make a diagnosis and start treatment. Regardless of how mild your symptoms feel, do not hesitate to seek an urgent appointment with healthcare workers.
Risk Factors
Bacterial meningitis is a highly contagious, though, fortunately, rather rare disease. Thus, all people who came in contact with it are at high risk of developing symptoms. Usually, it takes from 3 to 5 days to start showing signs of the infection after the first contact with the bacteria.
Young children and babies, in particular, are most at risk for this disease. It spreads faster and proceeds to severe stages rather quickly. People who spend most of their time indoors, in large groups (such as at schools or large gatherings) are also at risk of contracting bacterial meningitis. Lastly, certain medication conditions, like having a low immune system due to HIV or operations, can increase one’s chances for meningitis.
Spreading
In most cases, bacterial meningitis is contagious and spreads easily, however, it is not always the case with this virus. For example, in one case, the disease can be spread via food. Though, a common way is to get infected from person to person. Respiratory fluids are often the major factor in the spread of the virus. Fortunately, timely antibiotic treatment reduces its ability to spread within 24 after starting the medication.
Although the disease spreads between people, being in large groups is enough for the virus to spread across the attendees.
Prevention
The best preventative method for bacterial meningitis is vaccination. Fortunately, we have vaccines that can prevent the four most deadly bacteria that start the disease. Sadly, these four vaccines won’t stop other bacteria from starting the disease. Yet, they can significantly lower the chances of getting infected or developing severe symptoms of the disease.
Additionally, people should consider droplet precautions and avoid physical contact with people with bacterial meningitis for at least 24 hours after the first treatment session.
As per usual, a healthy lifestyle can enhance your chances of getting bacterial meningitis or having an easier course of the disease.
Final Thoughts
Bacterial meningitis is a dangerous disease that can have severe consequences on one’s health. The virus spreads easily and fast, affecting the young and those with the weakest immune system first. It progresses rapidly, which leaves people little time to spot symptoms and seek professional medical care on time. Untreated for a long time, the disease can lead to brain damage or death.
Fortunately, this form of meningitis is one of the rarest. In addition, people can get vaccinated against most bacteria that start such a disease. Lastly, people should also be careful in large gatherings of people, consider droplet precautions and lead a healthy lifestyle to enhance their personal chances of fighting the disease.