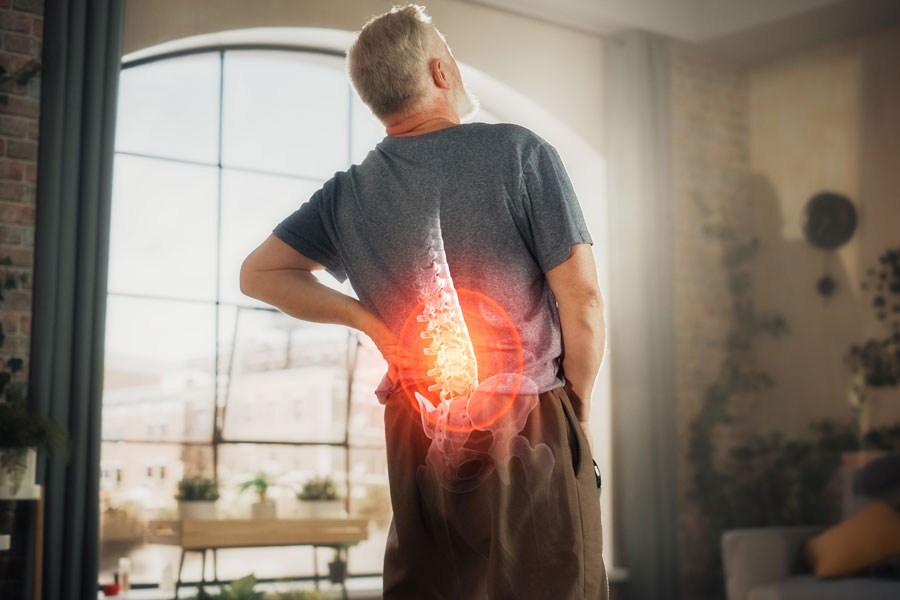
Pain in spine is one of the most common orthopedic problems in the world. Some scientists claim the global lifetime prevalence of back pain is 84%, which means almost every adult person experiences backache at least once in a lifetime. Other statistics say that 23% of adults suffer from chronic spinal pain. In the United States, 39% of the adult population suffers from pain in the spine.
With the growing concern around this problem, we’ll try to figure out the causes of pain in the spine and the risk factors promoting the development of such conditions. Finally, we’ll name some treatment options that your doctor may recommend.
Risk Factors for Back Pain
Before we get down to specifying the reasons for backache in adults, let’s take a brief look at the risk factors that elevate your chances of getting into the statistics given above.
- Aging. According to the CDC, people aged 65+ are more prone to developing back pain.
- Gender. Women suffer from pain in the spine more often than men. This is explained by the structural differences of the pelvis, hormonal fluctuations in women, and the consequences of pregnancy and childbirth.
- Ethnicity. Non-Hispanic white people suffer from back pain more often that representatives of other ethnicities.
- Level of income. This must be surprising but people with a lower income develop spinal pain more often than those making more money. This can be explained by the working conditions and the level of physical load these people get at work.
- Body mass. A healthy weight is essential for a healthy spine. Excess mass increases the load on the backbone, thus provoking the development of certain orthopedic disorders.
- A lack of muscle strength. Muscle weakness causes increased load on the backbone, promoting pain.
- Certain medical conditions. Some types of arthritis and malignancies can cause mild-to-severe backache.
- Smoking. There is sufficient scientific evidence of smoking associated with back pain. The prevalence of backache in smokers is 28%. It’s also worth mentioning that the incidence of spinal pain grows with the growth of smoking exposure.
Knowing Where It Hurts. Spine Regions
Our backbone plays an essential role in the body. It supports our upper body, head, and shoulders allowing us to walk upright. This organ consists of 33 vertebrae, which form a tunnel where our spinal cord runs, spreading the nerves throughout our body.
Between each vertebra, there is a disk, which adds flexibility to the backbone and works as a cushion that prevents vertebrae friction and, therefore, deformation.
Starting from the top to bottom, our backbone is divided into four regions: cervical (neck), thoracic, lumbar (lower back), sacrum, and coccyx.
Causes of Spinal Pain
The variety of health conditions that may provoke pain in the spine is numerous, so we’ll concentrate on those diagnosed most often.
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis is an inflammatory disease and a type of arthritis. This disorder usually starts with the feeling of soreness and stiffness in your hips and lower back, which is usually worse in the morning. If left untreated, this disease causes permanent damage to your backbone, leading to vertebrae fusions. What’s more, it spreads up your spine and may affect other bones and joints in the body. One of the typical visible symptoms of this disease is that the person gets a hunchback.
Herniated Disk
The incidence of herniated disks ranges between 5 and 20 people per 1000 adults. Most often, this disk disease affects people between the ages of thirty and fifty. This disorder usually appears due to excess stress on the disks, like when you lift heavy weights. With age, disks in your backbone lose their initial properties and get drier, and therefore, more prone to injury. When the disk breaks or tears, you get this disease. The symptoms of a herniated disk may include leg pain and the feeling of numbness or tingling in the limbs.
Spinal Stenosis
One of the essential functions of the vertebrae is to form a tunnel for the spinal cord. If, for some reason, the space within the vertebrae shrinks, the pressure of the bones on the spinal cord and nerve roots increases, provoking spinal stenosis. This condition may show through pain in the spine, tingling, numbness, and muscle weakness. Still, some people may not have any symptoms. Spinal stenosis usually affects the cervical and lumbar areas of the spine.
Cauda Equina Syndrome
Another orthopedic condition that may affect your peripheral nerves is cauda equine syndrome. Cauda equine refers to a group of nerves coming from the lumbar cistern, which is the area between the end of the spinal cord and the end of the vertebral column. Certain types of spinal injuries and disorders may cause the pressure on these nerves to grow, triggering cauda equine syndrome. If this occurs, a person loses control of the lower body functions, including bowel movements, bladder control, and walking. Unlike other disorders on the list, this one requires emergency surgery.
Sciatica
The pressure on the sciatic nerve caused by the herniated disk or other spinal conditions causes the disorder called sciatica. Its typical symptoms include pain shots that go through your bottom to the legs. Sciatica affects only one side of the body, so that’s the distinctive feature of this disorder.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Pain in Spine
The diagnostics of spinal conditions depend on the symptoms you have. In some cases, it’s enough for a doctor to know your symptoms, though in most cases, you’ll have to pass a CT scan, an X-ray, or another diagnostic procedure that will allow the medical specialist to visualize your backbone and nerves.
Based on the problem you have, your healthcare provider may offer conservative treatment or surgery. With herniated disk and spinal stenosis, you may be offered to start conservatively, and only if you don’t respond to that therapy, your doctor will probably suggest surgery.
You can also make use of the following advice, which should help you soothe the pain and improve your quality of life:
- start physical therapy;
- limit the physical load on the spine;
- work on the back muscles to support the spine;
- eat healthily and get enough vitamin D to strengthen your bones;
- keep your weight within the recommended limits;
- take painkillers to reduce pain;
- do some stretching exercises to enhance your spine flexibility;
- get enough rest if your pain is sharp or acute.
Prednisone for: arthritis, spondylitis, relapsing polychondritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, vasculitis.
Bottom Line
Pain in the spine is a common problem among people of all ages. Most of them appear due to uncontrolled load on the spine and are preventable. Take care of yourself, and remember, if you don’t care about your health, nobody will.